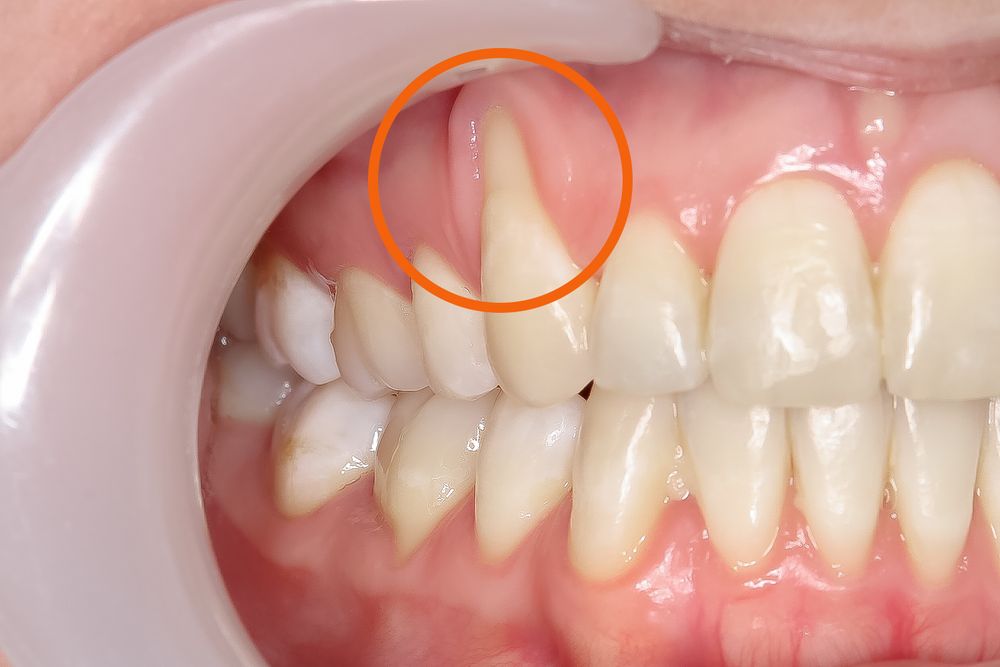
The most common causes of receding gums are:
- Periodontal Diseases – Bacterial infections destroy gum tissue and the supporting bone that holds the teeth in place. Periodontal diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis, a more advanced form of gum disease, are the main causes of receding gums. Because the gums are the Skin of Your Teeth, it’s essential to take care of the gums to protect the teeth.
- Poor Dental Hygiene–Dental plaque, a biofilm that covers the teeth, consists of bacteria and the sticky substances they secrete. Inadequate brushing and flossing permits plaque to accumulate, causes cavities and erosion of enamel, and eventually hardens into tartar. Tartar must be removed by a dentist or dental hygienist. If the tartar collects above the gum line, it can cause gingivitis, receding gums and gum disease.
- Brushing Harshly – Using excessive force to brush the teeth may damage both the enamel of the teeth and the gums themselves. A soft toothbrush is best to remove food and stimulate the gums. The PeriClean Ultra-Soft Toothbrush, designed by a dentist, will help keep teeth clean and gums (the Skin of Your Teeth) healthy.